Role and Importance of SMEs in the Indian Economy
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of India’s economy, playing a crucial role in driving economic growth, employment generation, and innovation.
As India marches towards becoming a $5 trillion economy, SMEs continue to contribute significantly across various sectors.
I. Definition of SMEs in India
The Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) classifies SMEs under three categories:
- Micro Enterprise: Investment in plant and machinery < ₹1 crore and turnover < ₹5 crore.
- Small Enterprise: Investment in plant and machinery < ₹10 crore and turnover < ₹50 crore.
- Medium Enterprise: Investment in plant and machinery < ₹50 crore and turnover < ₹250 crore.
II. Contribution of SMEs to the Indian Economy
SMEs play a vital role in multiple aspects of the Indian economy, as reflected in the following key contributions:
1. Contribution to GDP
SMEs contribute
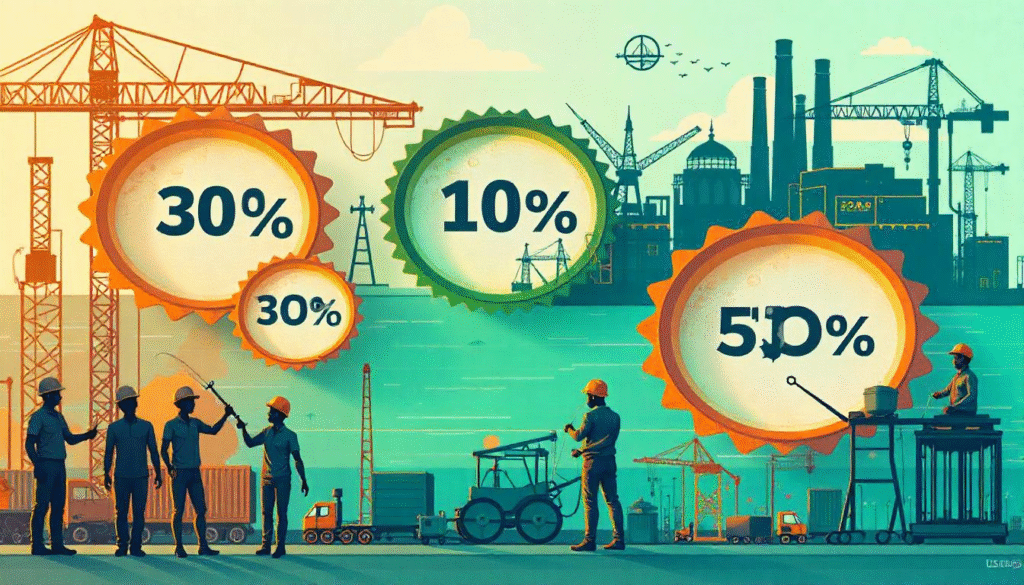
- approximately 30% of India’s GDP.
- 45% of total output in manufacturing sector.
- 25% of total GDP in services sector.
2. Employment Generation
- SMEs are the second-largest employer in India, after agriculture.
- As of 2023, the MSME sector employed over 110 million people across urban and rural areas.
- SMEs significantly reduce regional imbalances by promoting inclusive development.
3. Export Contribution
- SMEs contribute nearly 50% of India’s total exports.
- Key sectors such as textiles, leather, handicrafts, and engineering products rely heavily on SME production.
4. Industrial Development
- SMEs contribute to over 40% of India’s total industrial output, fostering local manufacturing.
- They support India’s ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiatives by enhancing domestic production capabilities.
5. Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- SMEs are hotbeds for innovation, especially in technology, IT services, and digital solutions.
- Government-backed incubators and innovation hubs help SMEs scale their creative solutions to larger markets.
6. Inclusive Growth
- SMEs empower marginalized groups, women entrepreneurs, and rural communities.
- SMEs provide an accessible entry point for small-scale investors and entrepreneurs.
III. Government Support and Initiatives
The Indian government actively supports SMEs through various schemes and initiatives to boost their growth:
1. Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs (CGTMSE): Provides collateral-free credit facilities for SMEs.
2. Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Offers easy finance for micro-enterprises.
3. MSME Samadhaan: A dedicated platform to resolve delayed payment issues for SMEs.
4. Startup India Initiative: Provides tax benefits, incubation support, and mentoring for emerging SMEs.
5. Udyam Registration: A simplified online registration process for MSMEs to avail government benefits.
IV. Empirical Evidence and Data-Backed Insights
Recent studies have reinforced the economic significance of SMEs in India:
- NASSCOM Report (2023): The Indian SME sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10% over the next 5 years, driven by digital transformation and export potential.
- RBI Data (2023): SMEs accounted for 17% of total bank credit in India, highlighting their significant role in the financial ecosystem.
- World Bank Report: SMEs in India show a 90% higher survival rate when supported by financial literacy programs and digital adoption.

V. Challenges Faced by SMEs in India
Despite their contribution, SMEs face multiple challenges:
1. Limited Access to Finance: SMEs often struggle with credit availability and high-interest rates.
2. Regulatory Complexities: Compliance issues with GST, taxation, and labor laws create operational hurdles.
3. Technological Lag: Many SMEs lack digital adoption, impacting their competitiveness.
4. Market Competition: Larger players often dominate pricing strategies, impacting SME profitability.
5. Lack of Skilled Workforce: SMEs frequently face difficulty in attracting and retaining talent.
VI. Future Outlook for SMEs
The future of SMEs in India looks promising, driven by:
1. Digital Transformation: With increasing digital adoption, SMEs are leveraging e-commerce platforms to expand their market reach.
2. Fintech Integration: Digital lending platforms are improving financial access for SMEs.
3. Global Expansion: SMEs are actively pursuing export markets, especially in sectors like IT, handicrafts, and engineering.
VII. Expert Opinions on SMEs in India
- Raghuram Rajan, Former RBI Governor:
“The SME sector is the backbone of India’s economy, and sustained growth depends on empowering these enterprises with better access to credit and technology.” - Nandan Nilekani, Co-founder of Infosys:
“Digital transformation is key to unleashing the potential of India’s SMEs, making them more competitive in global markets.” - Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw, Chairperson of Biocon:
“SMEs are the driving force of India’s innovation ecosystem. Supporting them will drive job creation and economic resilience.”
VIII. Conclusion
SMEs are integral to India’s economic fabric, contributing significantly to GDP, employment, exports, and industrial output. As India progresses toward global economic leadership, empowering SMEs with better financial support, digital integration, and policy reforms will be crucial.
By fostering innovation, promoting inclusive growth, and overcoming operational challenges, SMEs can truly unlock India’s economic potential and shape a sustainable future